This page was last updated on June 3, 2024
William A Bacon's Home Pages/Space Exploration sub Page

Comments?????
Email the Webmaster!!!!!
Page Table of Contents
- Return to Domain Home page
- Return to Domain Directory Page
- Introduction to space
- The Frontier Fields Initative
- Launching into Space!
- The ARTEMIS Missions
- Mission to the International Space Station
- My OBSERVATORIES Page!!!
- The Hubble Space Telescope
- The Subaru Telescope
- THE James Webb Telescope
- The High Definition Space Telescope
- The Lisa gravitional wave observatory pathfinder
- Types of Observatories
- Exploring the Solar System
- Private efforts to get into space
- Speculation
- NASA's ORION Nuclear rocket proposal
- Training for space
- Links to NASA!
- NASA Specialty sites
- Information on Mars
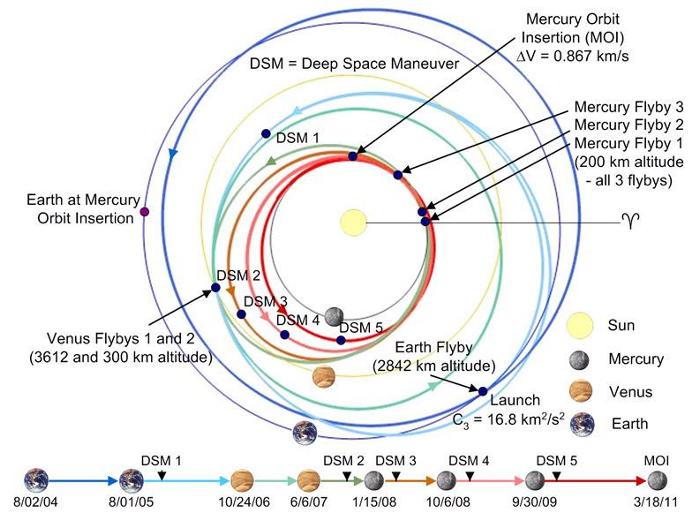
- Information on Mercury
- My Missions to the Universe page
- My page on Comet 67p of the summer of 2014
- Space News
- Space ref group of sites and additional informational sites
- Space advocacy Groups
- The National Space Society
- Material on the moon
- Information related Earth and Space Weather
- EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES FROM Educator Labs
- Misc. Education Resources
- Education Resources from Math Camps
- Informational/Reporting Sites
- METAPHYSICAL ASPECTS
- PHYSICS
- Four new missions for NASA
- The Outer Space Treaty was Signed in 1967. Can it Handle the Future of Space Exploration?
- Getting To Mars Quickly With Nuclear Electric Propulsion
- Misc. Articles
- Jump To the FLATARTICLES subsection
- Jump To the Pdfs subsection
- Returning from Space
- Click here to go to the bottom of this page"
INTRODUCTION to space!!!!
Current status of the deep space network
About the Deep Space Network: Space Communications and Navigation
Information on About the Deep Space Network: Space Communications and Navigation
NASA's Digital Orrery
MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes
Find Starlink!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
UNITED NATIONS TREATIES AND PRINCIPLES ON OUTER SPACE
Information on UNITED NATIONs TREATIES AND PRINCIPLES ON OUTER SPACE (PDF)
Cool Worlds
The space war website
R00t.cz
information on amatuer rdio nerds on cracking space telemetery
Speculation
Jobs In Space
Go to to get a 30-day free trial and 20% off their annual subscription. We all dream of a future in space, but it will take a lot of work to get there and more to make it a place we can visit and live. Of course, where there’s work to be done, there’s jobs to be had. Join this channel to get access to perks: / @isaacarthursfia Join this channel to get access to perks:/ @isaacarthursfia Visit the sub-reddit Visit our Website: Join Nebula Support us on Patreon: : Support us on Subscribestar / isaacarthur Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264 Reddit: Twitter:on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server: Credits: Jobs in Space Episode 449b; June 2, 2024 Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator
Click here to return to top of page
NASA has too Many Spacecraft to Communicate With. Time to Build More Dishes
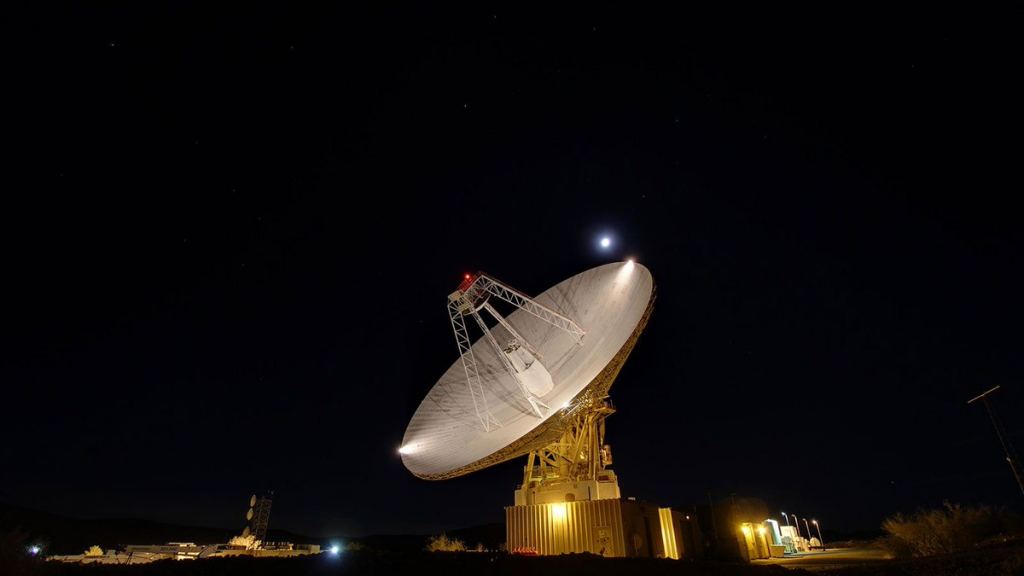

70-m dish of the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex, located near Barstow, CA. Credit – NASA / JPL – Caltech NASA is a sprawling organization that has to talk to everything from politicians in Washington DC to space probes that have left the solar system. Discussions with the first might be as simple as a written letter for informal conversation, while the second requires a high-power network of ground-based antennas. Known as the Deep Space Network (DSN) this series of antennas spread over three continents is the backbone of NASA’s communications with its various space probes. Now the DSN is in the process of implementing a well-deserved upgrade.
Explore NASA’s 70-Meter Deep Space Communications Dish (360° Video)
Explore NASA’s massive 70-meter deep space communications antenna located at the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex in Barstow, California. This antenna is part of the Deep Space Network, NASA’s international network of facilities used to communicate with faraway spacecraft exploring our solar system. The antennas of the Deep Space Network are the indispensable link to robotic explorers venturing beyond Earth. They provide the crucial connection for commanding our spacecraft and receiving their never-before-seen images and scientific information on Earth, propelling our understanding of the universe, our solar system and ultimately, our place within it. To learn more about the Deep Space Network, visit
DSN Uplink-Downlink – New NASA Game
Play DSN Uplink-Downlink at Find more fun videos, games, and articles about space and Earth science at

Graphics posters showing the three 70-m antennas that are part of the DSN. Credit – NASA / JPL-Caltech
Click here to Jump to Associated Universe today's pages
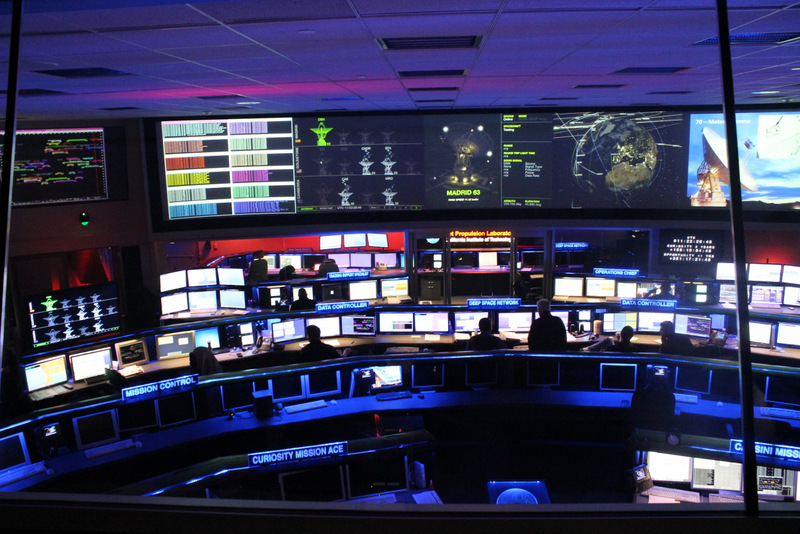

A view of the Space Flight Operations Facility at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory,
where all the data going both to and from all planetary missions is sent and received via the Deep Space Network.
Credit: Nancy Atkinson.
THIS IS THE COOLEST! EVERYTHING THAT’S ORBITING THE EARTH RIGHT NOW
Stuff in Space. This is everything that's orbiting the Earth right now.
Credit: James Yoder
An Upcoming Mission is Going to Assemble and Manufacture a Communications Antenna and Beam in Space
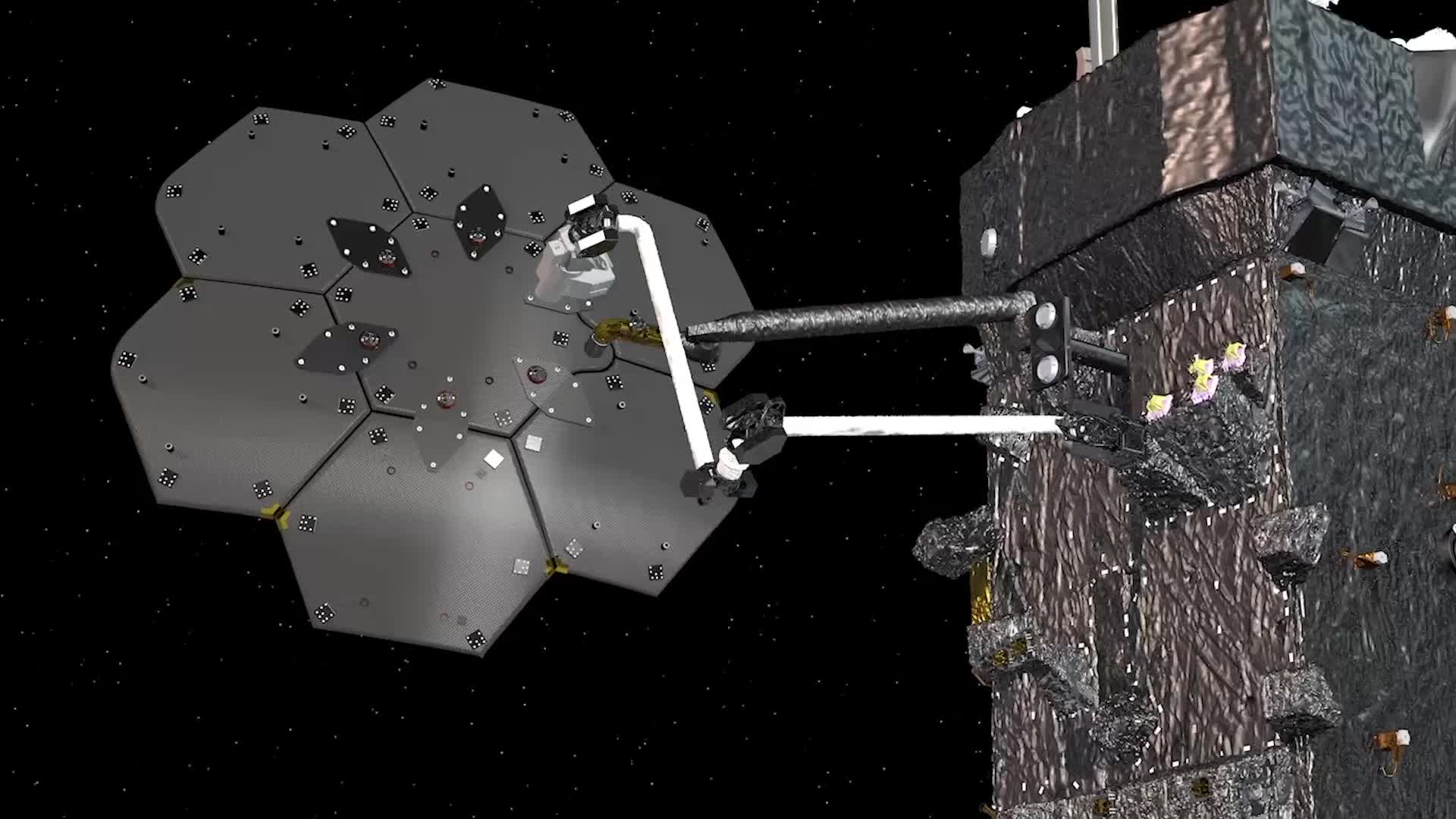

It has been suggested that if humanity wants to truly embark on a renewed era of space exploration, one of the key ingredients is the ability to manufacture structures in space. By assembling everything from satellites to spacecraft in orbit, we would eliminate the most costly aspect of going to space. This, simply put, is the sheer expense of escaping Earth’s gravity well, which requires heavy launch vehicles and LOTS of fuel!
As part of a $142 million contract signed with NASA, SPIDER will assemble seven elements to form a 3-meter (9-foot) communications antenna that will communicate with ground stations in the Ka-band. It will also construct a 10-meter (32-foot) lightweight composite spacecraft beam – using technology developed by Washington-based aerospace company Tethers Unlimited – to demonstrate that structures can be built in space.
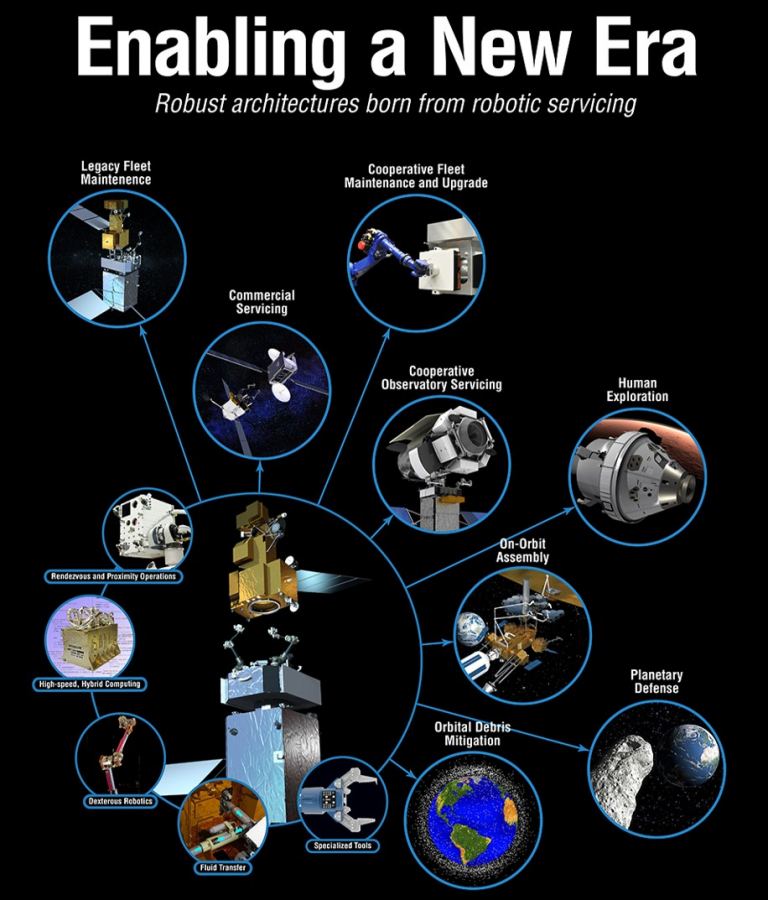
Infographic detailing the benefits of satellite servicing. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SSPD
Click Here to return to Page Index
ORION: NASA'S Nuclear Rocket Proposal

Image: Project Orion concept. Image Credit: Adrian Mann.
At their most fundamental level, all rockets past and present were and are, basically, controlled bombs.
Their fuel consists of materials and chemicals which, when activated/combined in the proper sequence and amount,
create a series of explosive reactions. The resulting energy release is then directed in a manner so that the resulting exhaust
comes out of the end of the rocket away from the payload sitting atop it and the direction that its builders want to send that payload.
That is essentially Sir Isaac Newton’s third law of motion put into practice.
Their fuel consists of materials and chemicals which, when activated/combined in the proper sequence and amount,
create a series of explosive reactions. The resulting energy release is then directed in a manner so that the resulting exhaust
comes out of the end of the rocket away from the payload sitting atop it and the direction that its builders want to send that payload.
That is essentially Sir Isaac Newton’s third law of motion put into practice.

Image: Artist’s rendition of NASA’s Project Orion. Credit: NASA.
The former Soviet Union had several real world examples of just such a catastrophe with their equivalent N1 rocket,
which they were using to compete with the United States in the race to place a man on the Moon by 1970.
Every one of their N1 tests (all unmanned) ended in dramatic failure, with one rocket explosion on the ground
practically vaporizing its launch pad and heavily cratering another pad with debris half a mile (almost one kilometer) away.
So now imagine a rocket design where the fuel used were actual bombs detonated on purpose –
and nuclear bombs at that. It was known as Project Orion.
which they were using to compete with the United States in the race to place a man on the Moon by 1970.
Every one of their N1 tests (all unmanned) ended in dramatic failure, with one rocket explosion on the ground
practically vaporizing its launch pad and heavily cratering another pad with debris half a mile (almost one kilometer) away.
So now imagine a rocket design where the fuel used were actual bombs detonated on purpose –
and nuclear bombs at that. It was known as Project Orion.
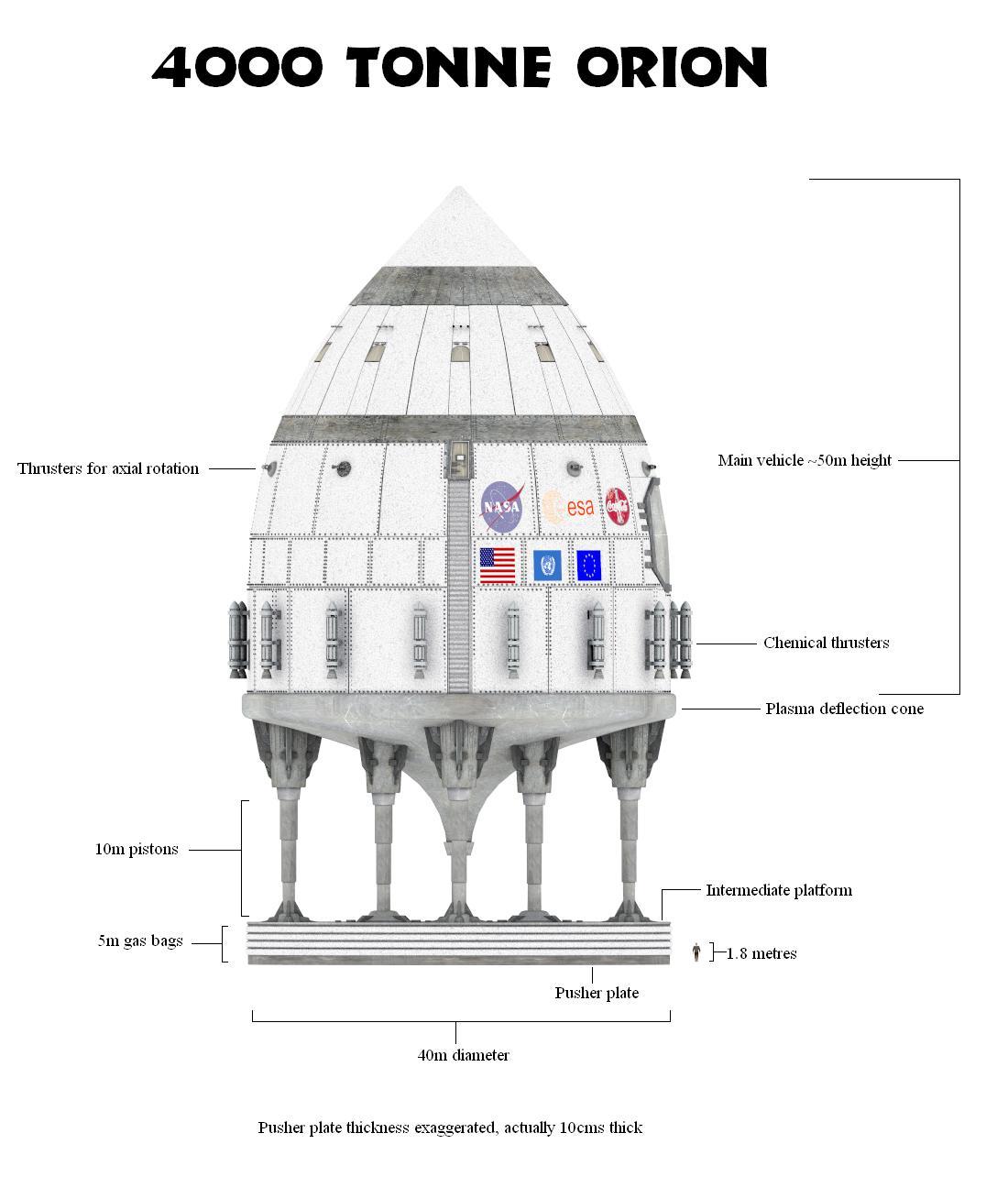
Image (click to enlarge). Credit: Rhys Taylor.
If nuclear power could be plausibly applied to mere ground transportation, then using it to send heavy space vessels
into the “final frontier” only made even more sense at the dawn of the Space Age. Both superpowers were cranking out those
very methods of propulsion at an ever-increasing rate.
In an example of turning swords into plowshares, Project Orion was envisioned as a vessel carrying a supply of hydrogen bombs
to be ejected out the stern of the spaceship one at a time. The bomb would then be detonated mere seconds later,
where the resulting plasma would encounter a large, thick, shock-absorbing “pusher plate” attached to the end of the spaceship
that would simultaneously allow Orion to be moved forward while protecting the ship from the blast and radiation.
Each new bomb detonation that followed would push the vessel faster and faster, allowing Orion to reach just about anywhere in the Solar System
within one year or the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, in just over one century under one mission scenario.
into the “final frontier” only made even more sense at the dawn of the Space Age. Both superpowers were cranking out those
very methods of propulsion at an ever-increasing rate. In an example of turning swords into plowshares, Project Orion was envisioned as a vessel carrying a supply of hydrogen bombs
to be ejected out the stern of the spaceship one at a time. The bomb would then be detonated mere seconds later,
where the resulting plasma would encounter a large, thick, shock-absorbing “pusher plate” attached to the end of the spaceship
that would simultaneously allow Orion to be moved forward while protecting the ship from the blast and radiation.
Each new bomb detonation that followed would push the vessel faster and faster, allowing Orion to reach just about anywhere in the Solar System
within one year or the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, in just over one century under one mission scenario.

Image (click to enlarge): General Atomics Orion spaceship concept. Credit: William Black.
The plans for Orion were anything but timid. Manned Mars missions using this vessel would have been sent in 1965,
followed by a mission to the ringed planet Saturn in 1970! The spaceship in the film 2001: A Space Odyssey, the USS Discovery,
was originally designed as an Orion type craft aimed at Saturn in the novel version. The author of the film’s screenplay and novel,
Arthur C. Clarke, was also a member of Project Orion. Not only could Orion have conducted a round-trip voyage to Pluto in just one year,
but Dyson also calculated a version that could flyby Alpha Centauri in about 130 years at 3% light speed.
By comparison, the Voyager space probes will take 77,000 years to reach the distance of our celestial neighbor 4.3 light-years away.
The team even considered a massive Orion that could serve as an interstellar ark, which became the vehicle of choice
in the 2014 television mini-series Ascension.
followed by a mission to the ringed planet Saturn in 1970! The spaceship in the film 2001: A Space Odyssey, the USS Discovery,
was originally designed as an Orion type craft aimed at Saturn in the novel version. The author of the film’s screenplay and novel,
Arthur C. Clarke, was also a member of Project Orion. Not only could Orion have conducted a round-trip voyage to Pluto in just one year,
but Dyson also calculated a version that could flyby Alpha Centauri in about 130 years at 3% light speed.
By comparison, the Voyager space probes will take 77,000 years to reach the distance of our celestial neighbor 4.3 light-years away.
The team even considered a massive Orion that could serve as an interstellar ark, which became the vehicle of choice
in the 2014 television mini-series Ascension.
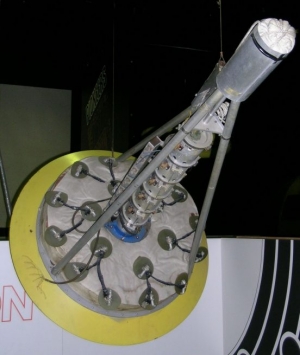
Image: Project Orion ‘Hot Rod’ Propulsion Test Vehicle. Credit: Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum.
In the end, Orion was terminated neither by physics nor technology but by politics and a growing public fear of nuclear power.
The Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty signed in 1963 forbids testing nuclear devices of any kind everywhere but underground.
Two years later, the USAF canceled the project’s budget. Orion became a legendary symbol of an era known for both
its far-reaching dreams and excesses of power. To this day, Orion is still the only feasible mean of interstellar travel,
both robotic and manned, that could actually be built with current (publicly available) technology and knowledge.
The Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty signed in 1963 forbids testing nuclear devices of any kind everywhere but underground.
Two years later, the USAF canceled the project’s budget. Orion became a legendary symbol of an era known for both
its far-reaching dreams and excesses of power. To this day, Orion is still the only feasible mean of interstellar travel,
both robotic and manned, that could actually be built with current (publicly available) technology and knowledge.
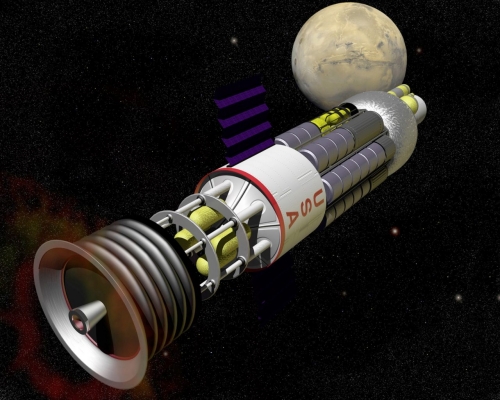
Image: Project Orion to Mars. Credit: NASA.
For more information on Project Orion, see the following:
Project Orion: The True Story of the Atomic Spaceship, by George Dyson, An Owl Book, Henry Holt and Company, New York, 2003.
These documentary videos on Project Orion here and here, and George Dyson TED Talk here.
For those want even more information about Project Orion and its variants, you must see Atomic Rocket’s pages on it here.
More links to updated information on Project Orion:
Thunderwell and nuclear Space
Winterberg Reinvents Project Orion
Updated Project Orion Nuclear Pulse
Winterberg Reinvents Project Orion
Updated Project Orion Nuclear Pulse
Click Here to return to Page Index
Training for space flight
at The Bucks County PA, National Aerospace Training center
AND NASTAR's parent Virgin Galactic
Click Here to return to Page Index
This section for NASA
Web site of the Jet Propulsion Lab
Click here for The
Current status of the deep space network

Here is:
NASA's NASA SPACEFLIGHT site
Here is: NASA's NASA SPACEFLIGHT site
Click Heree for NASA's Themis' Mission
Click Here for Nasa's Solar System Simulator
This is NASA's New solar system simulator EYES on.....
And here for NASA's NASA's science for all
This site simulates Meteor Impacts
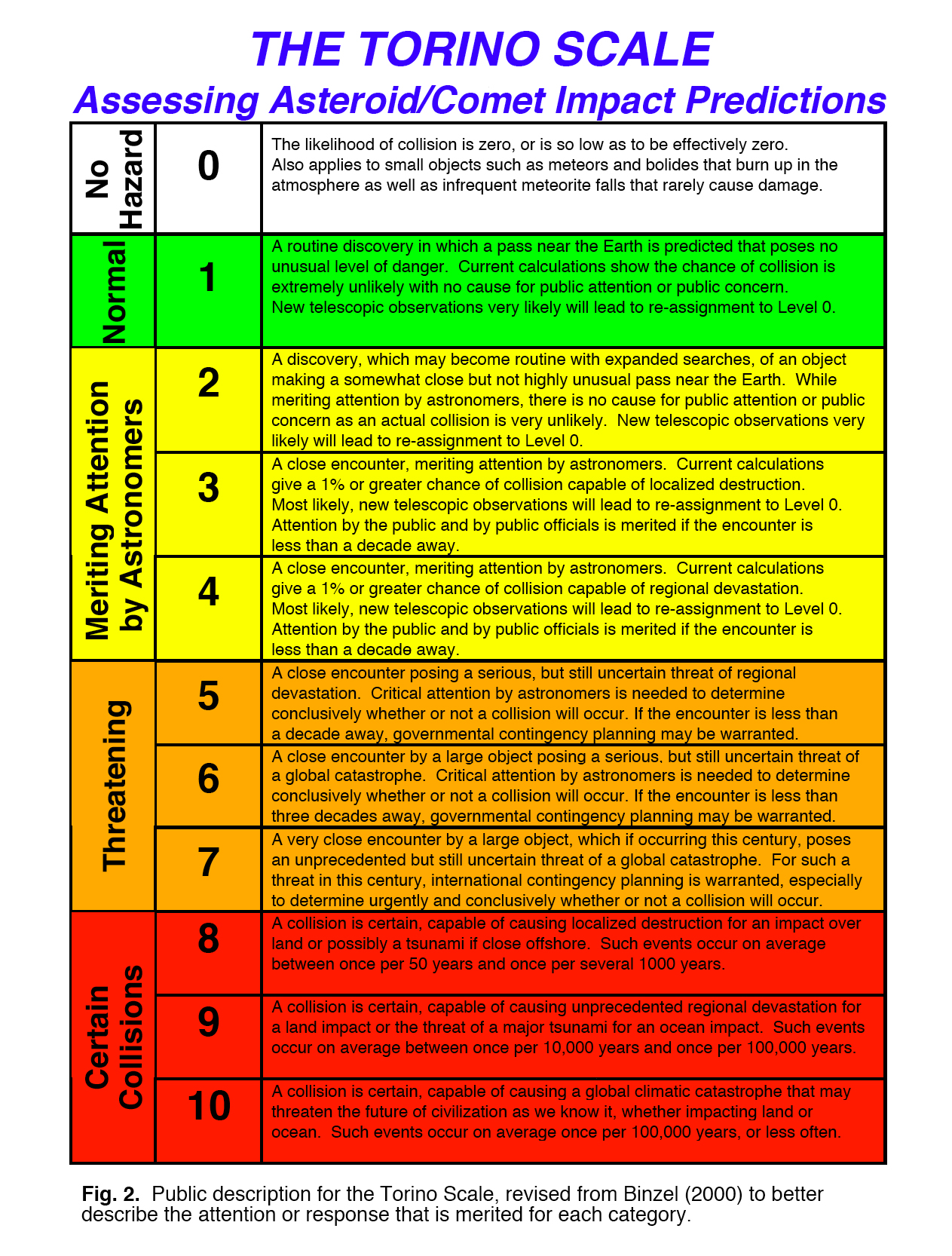
Here is NASA's site for risks associated with The Rsks of near earth objects colliding with earth
Here is the site for NASA's
Torino_scale.html"
For now the only way to get into space is the Space Shuttle Countdown site
For a contray look at Nasa it's NASA Problems!!!
Here is travel information to Kennedy Space center.com
Here is NASA's attempt at antigravity Anti-Gravity and perpetural motioJJn
Here is a competitor to NASA It's Arianespace of Europe
To help bring down the cost of space travel Click Heree for The X Prize contest to bring down the cost of Space
Here is where you train for space At Space Flight Training.com
Here is a free orbital Simulator
And here is Nasa's Spaceflight center
Here is the
Home page for the international space station
If want to view some up to date photos of our solar system, here is Nasa's PhotoJournalism site
Here is NASA's search site Search NASA
A Jandiced view of NASA NASA watch
Here is Hobby Space
Yet another interest is outer space exploration; I Have hot-links to help you explore!
Here is an inreresting uk site Darkstar
To begin with, here is NASA's HQ page N A S A's H Q.
You can monitor Space Shuttle Missions as they fly from here! Shuttle Mission control
This Nasa site site helps you to OBSERVE THE EARTH
This site to observe the sun it's The official SOHO site!
In order to explore space you must go faster than light! NASA's interstellar page
Click Here to return to Page Index
NASA's SPECIALTY SITES
NASA's Free Data access SITE
Click here for NASA's Free Data access SITE
NSAS'S latest Addition History of the Space Program in free e-books!!!!!
Here is NASA's Hubble Heritage site
AND here is NASA's Nasa's time series Slide show
Here is NASA's Deep Space Network
AND NASA's Solar System by NASA!
AND NASA's Planetary data system
Here is Nasa' Near Earth Objects Observatory
This is JPL's site J P L's H Q
Here for weather in space Space weather
This site for NASA's Science site
Here is NOAA's Space weather site
Here for NASA's Observation site
Here is rasc-al Revolutionary aerospace systems concepts academic linkabe
An online training The largest Space NGO in the U.S the Kepler Space Institute
You track satellites Here
NASA's Image database site
Information on NASA's Image database site
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
Take our visualization tour: "Illuminating the Invisible
Click Here to return to Page Index
M A R S
This section to track the Spirit space probe to Mars(By Computer simulation from NASA)
First the NASA page for the spirit probe(Click Heree for simulated tracking) The Spirit is launched to MARS!
What the Martians think of Curosity!!!


How cool is this? An animation of seven images from the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
show a �flapping� of the parachute that allowed the Curiosity rover to descend safely through Mars atmosphere images.
The chute, imaged as it lay on the ground following the rover�s safe landing, was blown about by the Martian breeze!
The images were acquired by HiRISE between August 12, 2012 and January 13, 2013. The different images show distinct changes in the parachute,
which is attached to the backshell that encompassed the rover during launch, flight and descent.
How cool is this? An animation of seven images from the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
show a �flapping� of the parachute that allowed the Curiosity rover to descend safely through Mars atmosphere images.
The chute, imaged as it lay on the ground following the rover�s safe landing, was blown about by the Martian breeze!
The images were acquired by HiRISE between August 12, 2012 and January 13, 2013. The different images show distinct changes in the parachute,
which is attached to the backshell that encompassed the rover during launch, flight and descent.
The Phoenix probe digs for ......

Weather on Mars!

First is a proposed flag for mars!

Fluid Evidence on Mars?
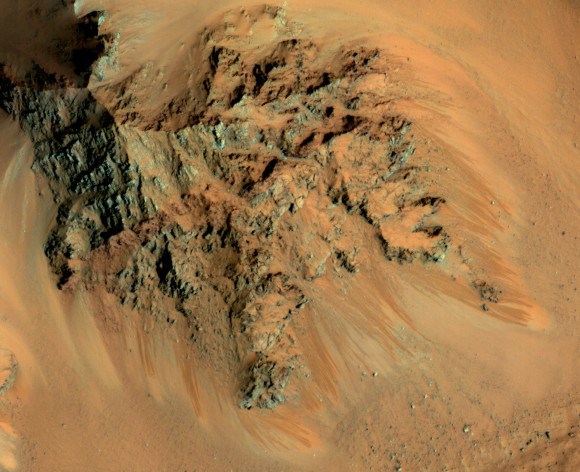
Is There Martian Salty Water At The Red Planet�s Equator? These Lines May Be The Smoking Gun!!!!!

A series of images from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE)
camera on NASA�s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter show how the appearance of dark markings on Martian slope
changes with the seasons.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona.
This Mountain on Mars Is Leaking
by JASON MAJOR on APRIL 11, 2015!

The web site of The Mars Reconnaissance Web Site"
Seasonal flows spotted by HiRISE on northwestern slopes in Hale Crater. (NASA/JPL/University of Arizona) As the midsummer Sun beats down on the southern mountains of Mars, bringing daytime temperatures soaring up to a balmy 25�C (77�F), some of their slopes become darkened with long, rusty stains that may be the result of water seeping out from just below the surface.
Explore Mars from Google.com map system!
And here is Mars Pedia.org
Here for University of Arizona Hires Mars Project!

And the Link to
The Cydonia Institute!!!
This web site is provided to the public for educational and research purposes
in the exploration of unusual structures found on Mars within the boundaries of the Cydonia area.
Independent articles are presented here in an effort to provide a venue for the comparative analysis of
NASA's photographs (Note; we have not altered any of the NASA source images presented on this site).
The public is free to use limited excerpts of our articles including text and images, as long as the author
and The Cydonia Institute is credited. The contents of this web site may not be reproduced or redistributed with
out the written permission from The Cydonia Institute. All articles on this site are condensed versions of larger manuscripts.
Additional text and images, for most articles, are available on request.
Be sure to bookmark this site; because new discoveries are being made all the time.
Amendments to current articles are also made periodically.
Director
George J. Haas
Associate Director
William R. Saunders
Members
Michael Dale
James Miller
Lee Bogart
The Cydonia Institute (Established 1991)
And the Link to The Cydonia Institute!!!
This web site is provided to the public for educational and research purposes in the exploration of unusual structures found on Mars within the boundaries of the Cydonia area. Independent articles are presented here in an effort to provide a venue for the comparative analysis of NASA's photographs (Note; we have not altered any of the NASA source images presented on this site). The public is free to use limited excerpts of our articles including text and images, as long as the author and The Cydonia Institute is credited. The contents of this web site may not be reproduced or redistributed with out the written permission from The Cydonia Institute. All articles on this site are condensed versions of larger manuscripts. Additional text and images, for most articles, are available on request. Be sure to bookmark this site; because new discoveries are being made all the time. Amendments to current articles are also made periodically. Director George J. Haas Associate Director William R. Saunders Members Michael Dale James Miller Lee Bogart The Cydonia Institute (Established 1991)
The High rise resolution imaging science experiment
a good way to begin is to look at a Context Camera(CTX) Image
to find interesting locations image map!
NASA Exploration of MARS
JPL's
Mars Rovers Site
Where are
MARS Rovers Now???
This for Cornell University's PANCAM
This section for all MER images!!!
This is the Archive for The Spirit Rover
This is the Archive for The Opportunity Rover
From this website You can explore mars Now!!
Another MArs Simulation mission The latest news about MARS ARCTIC 365!
And here is Mars Home.org
Check this web site for is NASA hacking the pictures?
Here is the Planetary Society's Aim For Mars.org website
The latest pictures from mars: Jpl Mars Gallery
Here is the outfiter you need to go to mars it's Starry night's Mars store
Here is a new effort it's The Mars Institute
This the website for
Here is the website for
The European Beagle probe
Here is
Mars TV
And another Mars news site:
It's Marstoday
Here is a great new site
It's Red Colony.com!
Here is
Red colony.com's Link page
Here is a site for
Martian Weather Report!
A special feature from Red Colony.com is the Mars Picture of the day!

Here is a Novel(?) about Mars it's The Mars Records!!
And A novel which reads like faction it's The Martian by andy weir
Here is Nasa's new Mars O Web Project
Here is Nasa Ames Homepage
Here is NASA's site for Nasa' Odyssey's space craft
Here is Themis' Mars 2001 Themis Data Distribution Site
Here is Odyssey's Themis camera
Here for an uncalibrated daily picture Visible light picture
Here for Odyssey's Neutron Spectrometer
Here is a German site asking What's going on on Mars???
Here is NASA's Mars Landing sites site
Click Here for Mars Observer Home page
Here is a web page for Science Headlines from NASA
Let's start with an upcoming movie about Mars! Mission to Mars
Here is another Mars organization It's the Mars Hill organization!
Here is the new One way trip to mars it's MARS ONE!!!
Click Here for The Planetary Society
THIS is the Planetary Society's Blog index page
Here is the Planetary Galaxy dynamics lab
another animation of 2010 TK7's wild orbit
The planetary Society of JAPAN
The Mars Society
NASA has a neat Mars Exploration site Center for Mars Exploration
Here is a page with which you can explore Mars!!!! The Mars Pathfinder Page
Nasa has another pathfinder page..... Mars global surveyor
Here is NASA's Mars Global Surveyor
The next surveyor Mission The Mars 2001 Mission
Another componet is the Mars rover The Mars Rover Site
Here are three sites from the Malin Space systems Co. Malin Site #1
This site #2 for Malin systems: Malin Site #2
This site #3 Planetary Mysteries
Another site for Malin Mars Pictures: Current Mars Pictures
This site is a simulation of mars on Earth The Artic Mars Simulation organization
This site is for the National Institute of Science and technology N.I.S.T
This section helps you find your new home on mars!
This page is a proposal for A Mars Government!
This site to help you locate The Red Colony
After you decide where you want to live on your new planet, Here for youre new house on Mars!

India is gearing up for its first ever space undertaking to the Red Planet dubbed the Mars Orbiter Mission, or MOM � which is the brainchild of the Indian Space Research Organization, or ISRO. Among other objectives, MOM will conduct a highly valuable search for potential signatures of Martian methane which could stem from either living or non living sources. The historic Mars bound probe also serves as a forerunner to bolder robotic exploration goals. If all goes well India would become only the 4th nation or entity from Earth to survey Mars up close with spacecraft, following(...) Read the rest of India�s First Mars Mission Set to Blast off Seeking Methane Signature